Zero-Training AI™
Intelligence Without
Data or Training
by Bill SerGio, The Infomercial King™
Additional information, live demos, and source code are available here:
- GitHub Project: https://github.com/tvmogul/AiNoData
- Demo Website: https://ainodata.com
- Main Website: https://ainetprofit.com/Patent
- YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/StationBreakTV
- Robot Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7_3RRghur1k
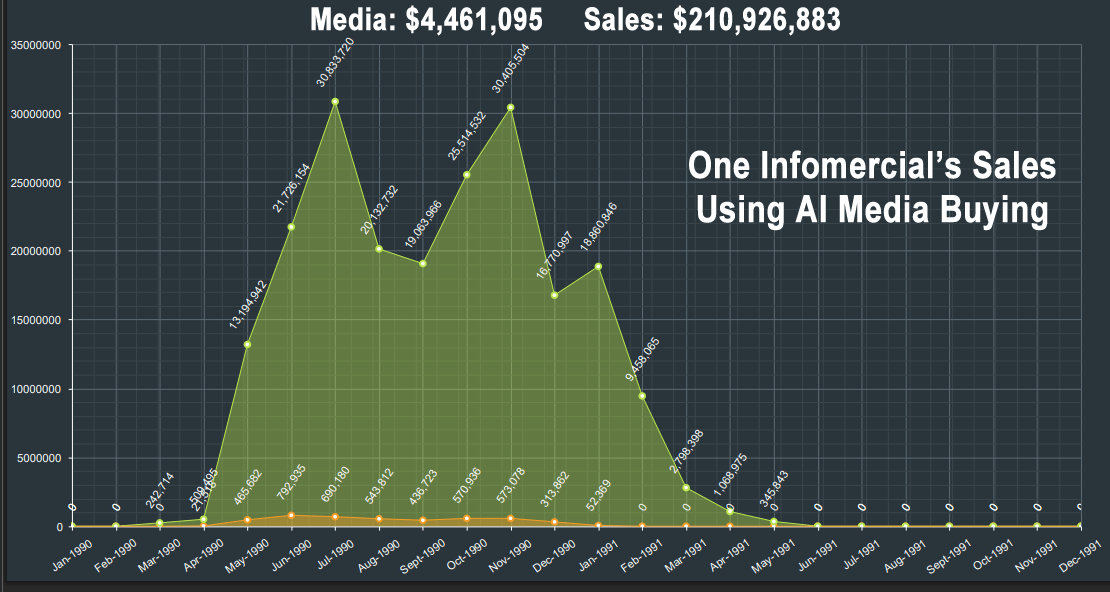
Introduction
The image above shows what was the results of using traditional AI Neural Networks to buy half hour television time for one of my company's infomercials. I should point that usng AI to buy media for infomercials is very complex in that it must consider there are so many additional income sources that are available from an infomercial such as television stations giving you a second half hour for FREE if you tell them that your client's show didn't make any money. Upsells of other products sold to callers when they place an order which can add thousands of dollars in addition profit to each sale. The AI system I developed considered all of these factors and more to achieve the results shown above.
The image below use my new type of AI called Zero-Training AI™ to run a media budget simulation that begins with $1,000 and, over the course of a simulated year, grows to typically over $60 million and that is what actually happens with infomercials if you apply the AI tools we devloped correctly. The results below do not include many of the other money-making realities of infomercials like "make goods" so the total gross sales at the end of a year are much less.
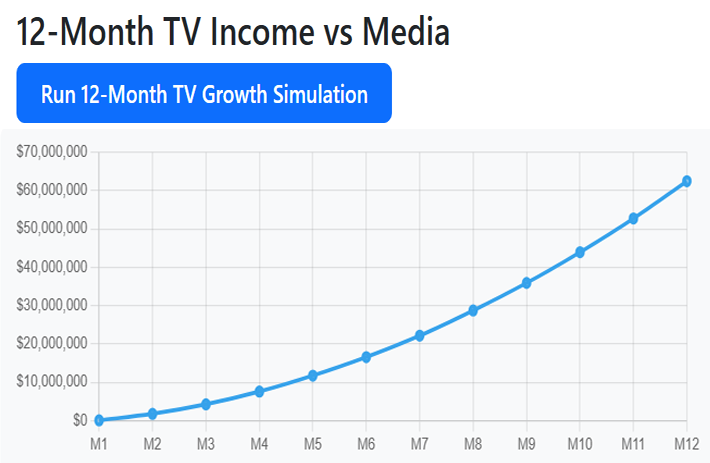
BUT this article is NOT about getting rich, media buying tactics, or financial advice. It is about a different way of building intelligent decision-making systems.
Check out the source code in the GitHub project linked above to see how the code works.
The image comes from one of four demos with source code in the GitHub project above built on an AI framework I created called Zero-Training AI™. The purpose of the demo is not to suggest that such outcomes are typical or realistic in practice, but to make a point very clearly: the system is making the best decisions without being trained on historical data.
Most modern AI systems rely on training — collecting data, fitting parameters, and retraining as conditions change. Zero-Training AI™ takes a fundamentally different approach. Instead of learning from past examples, it computes decisions directly from structure, constraints, and objectives defined by the problem itself.
This article introduces that framework, explains how one of the demos works, and shows how the same approach applies far beyond media buying.
Background
My academic background is in advanced mathematics and theoretical physics, followed by medical school. After medical school and clinical training, I founded and operated a company that sold medical supplements via national television advertising.
In that business, media buying decisions had to be made continuously under uncertainty: budgets were limited, outcomes varied by station, and conditions changed week to week. I experimented with neural networks I wrote and trained models to optimize decisions. They worked — but they were slow to adapt, expensive to maintain, and opaque.
That experience raised a simple question: why does decision-making require training at all? In many real-world systems, the governing constraints and objectives are already known. Physics does NOT train on past trajectories to decide how a system should evolve; it follows equations derived from structure.
Zero-Training AI™ grew out of that observation. Instead of fitting a model to historical data, the framework defines a structured Decision Space™ governed by explicit mathematical relationships. Decisions emerge by resolving tradeoffs and constraints directly, rather than by inference.
In this framework, intelligence is not learned from examples. It is produced through deterministic computation. Once the structure of the problem is defined, outcomes follow from mathematics itself, without retraining, recalibration, or statistical approximation.
I call this mathematical domain I invented Decision Space™ but is not a dataset, model, or parameter set. It is an abstract, structured space in which every point represents a valid candidate decision subject to known constraints, limits, and priorities.
Rather than learning how to act from historical examples, Zero-Training AI™ operates by evolving a decision state directly within Decision Space™. Movement through this space is governed entirely by explicit mathematical structure — objectives to optimize, constraints to satisfy, and penalties to avoid — all defined up front by the problem itself.
Because Decision Space™ is constructed from known rules instead of learned correlations, the system does not require training, retraining, or probabilistic inference. When conditions change, the governing equations change, and the resolved decision state changes immediately as a consequence of the mathematics.
Why This Is Artificial Intelligence
This system is artificial intelligence by any rigorous definition. It autonomously evaluates alternatives, resolves competing objectives, enforces constraints, and adapts its decisions in real time as conditions change. It does so without human intervention, fixed rules, or pre-scripted outcomes.
Artificial intelligence is not defined by training data, neural networks, or statistics. It is defined by autonomous decision-making. Zero-Training AI™ continuously analyzes a high-dimensional Decision Space™, selects actions that optimize objectives, and responds intelligently to new inputs. The absence of training data does not disqualify it from being AI; it removes an unnecessary dependency.
In fact, many classical AI systems predate modern machine learning and operate entirely through reasoning, optimization, and constraint satisfaction. Zero-Training AI™ belongs to this lineage — an intelligence that emerges from structure, not from accumulated examples.
This Is NOT an Algorithm
Zero-Training AI™ is not an algorithm. It is not a sequence of procedural steps that transform inputs into outputs. There is no fixed recipe, rule chain, decision tree, or flowchart that determines behavior.
Instead, the system defines a mathematical decision landscape. Within that landscape, outcomes are resolved by minimizing constraint violations and optimizing objectives. The computation does not “execute instructions” in the traditional sense; it settles into a decision state dictated by the governing structure of the problem.
This distinction matters. Algorithms prescribe how to reach an answer. Zero-Training AI™ defines what must be true, and lets mathematics determine the result. The intelligence is not in the steps — it is in the structure.
Using the Code
The demo code accompanying this article is implemented as a standard .NET web application. It is intentionally compact and readable, not because the underlying ideas are simple, but because the framework expresses decision-making through structure rather than procedures.

At a high level, the system defines:
- A set of decision variables (allocation weights)
- Explicit constraints (budget conservation, limits, feasibility)
- An objective structure (profitability, stability, persistence)
- A deterministic evolution rule that resolves decisions in real time
There is no training phase, no historical data, no model fitting, and no learned parameters. Each simulation step recomputes the decision state directly from the current conditions.
Conceptually, the engine operates by constructing a mathematical decision landscape and resolving a state within that landscape. In simplified form, the system evaluates a function of the form:
F(q, p) = (1/2) Σ pᵢ² − α Σ (Vᵢ · qᵢ) + λ ( Σ qᵢ − 1 )²
Where q represents decision weights, p represents internal momentum,
V encodes value signals derived from the environment,
and α and λ control reward strength and constraint enforcement.
-
Virepresents the realized pull ratio of channel i — a measured return per dollar that remains approximately stable over a finite time window -
qirepresents the fraction of capital allocated to that channel -
The optimization does not predict
Vi; it assumes short-term repeatability based on observed outcomes -
Minimizing
F(q, p)reallocates capital toward higher-return channels while enforcing budget conservation - No probability distributions, training data, or learned parameters are required — only realized returns and explicit constraints
This expression is intentionally incomplete. The novelty of Zero-Training AI™ is not the existence of an objective function, but how such functions are constructed, coupled, and resolved dynamically within what I call Decision Space™. Those details are part of a Patent Pending framework and are demonstrated behaviorally rather than disclosed procedurally.
In practice, the system evolves its internal state to reduce constraint violations and favor higher-value outcomes simultaneously. The result is a smooth, stable reallocation of resources that adapts immediately when inputs change — without retraining, recalibration, or statistical inference.
var result = allocator.RunSimulation(
initialBudget,
months,
newStationsPerMonth,
cancellationRate,
showType,
monthlyPrice,
yearlyPrice,
timeSteps
);
Advertising decisions are often treated as inherently unpredictable. In practice, response behavior is locally stable. When the same creative is purchased on the same outlet, the realized pull ratio (return per dollar of media) is approximately repeatable over a finite time window. This repeatability is sufficient to support deterministic optimization.
Rather than predicting outcomes, the system reallocates capital based on realized returns. Given stable response ratios and known constraints, optimal allocation becomes a deterministic decision problem rather than a probabilistic inference problem.
The media-buying example exists to make the behavior visible and intuitive. The same engine can be applied to control systems, resource allocation, decision governance, robotics, or any domain where constraints and objectives are known and deterministic behavior is required.
The purpose of the demo is not to reveal the full mathematical machinery, but to show that intelligent decision-making can emerge directly from structure — without training data, learned models, or opaque inference layers.
Additional Demonstration Applications Included
The demo project accompanying this article contains several additional, self-contained demonstrations that apply the same Zero-Training AI™ decision framework to very different problem domains. Each demo is intentionally simple in presentation while illustrating a core property of the framework: deterministic, real-time decision resolution without training data or learned models.
Together, these demos show that the same mathematical decision framework can be applied across allocation, control, governance, and stabilization problems, all without training data, probabilistic inference, or learned representations.
LLM Token Governor (Hallucination Control Demo)
In this demo, the user enters a natural-language prompt. A language model produces multiple candidate sentence continuations for the same prompt. These candidates are not generated or modified by Zero-Training AI™.
Instead, Zero-Training AI™ operates as a deterministic governance layer on top of the model output. Each candidate is evaluated within a structured Decision Space™ that encodes consistency, constraint compliance, and safety criteria. The system then selects and highlights the candidate that best satisfies those constraints.
This demonstrates how Zero-Training AI™ can be used to govern generative models— reducing hallucination risk and enforcing consistency—without retraining, fine-tuning, or altering the underlying model.
Drone Hover Stabilizer Simulation
This demo presents a simplified visual model of a quad-drone attempting to maintain a stable hover orientation. The user can introduce disturbances such as simulated wind gusts or external torque.
The system responds by deterministically resolving a new stable control state in real time. The visual representation shows orientation changes and relative control energy, not a physical flight simulation.
This example illustrates how Zero-Training AI™ can function as a real-time control and stabilization system, computing corrective actions directly from structure and constraints rather than from learned dynamics or historical flight data.
Robot Arm Balancer
This demo features a simple two-joint robotic arm tasked with maintaining or reaching a target position. When the user moves the target, the arm smoothly transitions to a new stable configuration.
No inverse-kinematics solver is trained, and no machine-learning model is involved. The arm’s configuration is resolved deterministically by minimizing constraint violations within a structured Decision Space™.
This demonstrates how Zero-Training AI™ can be applied to mechanical control and coordination problems, where stability, smooth motion, and explainability are more important than pattern recognition.
Beyond mechanical control, the same decision framework applies to robot companions and human–robot interaction. In this context, Zero-Training AI™ does not generate language or emotions; instead, it operates as a real-time decision governor that selects responses based on conversational constraints, consistency, intent, and social context.
Rather than predicting dialogue from training data, the system resolves each conversational turn as a stable decision state within a structured decision space. This allows a robot companion to respond to a human in a manner that is coherent, context-aware, and responsive to the full range of human social cues and situational interpersonal context — much like another human — without requiring conversational training, large language models, or probabilistic inference.
Points of Interest
Several things may stand out to experienced developers:
- No datasets are loaded or trained against
- No probabilistic inference is used
- Behavior changes immediately when inputs change
- The system remains explainable at every step
One interesting discovery during development was that many problems commonly handed to machine-learning models behave more predictably — and more robustly — when expressed as constrained mathematical systems instead.
The dramatic numbers in the budget demo are not the point. They exist solely to make the system’s behavior visible and intuitive. In real-world deployments, successful half-hour infomercial campaigns can operate at much higher revenue levels than those shown in the budget demo. The absolute magnitude is intentionally constrained in this demo so that the dynamics of the decision process can be inspected clearly. The underlying mathematics behaves identically at larger scales — only the numerical magnitude changes, not the structure or behavior of the system. The real takeaway is that decision-making does not have to be statistical, and intelligence does not have to be trained.
Future Direction – Comprehensive Applications of Zero-Training AI™
Zero-Training AI™ is a versatile foundation for any domain where constraints, objectives, and real-time response are critical. Below is a detailed overview of major applications, with descriptions and illustrative images.
1. Disaster Relief & Humanitarian Logistics (ReliefScope)
Optimizes truck/personnel/supply allocation from known inventories and real-time inputs (assessor reports, drone imagery, road status). Resolves maximal impact under hard constraints (fuel limits, priority levels, accessibility) in seconds — fully auditable for NGOs like the Red Cross.

2. Home & Community Energy Management
Balances solar generation, battery storage, and household demand under physics-based constraints (weather forecasts, pricing, blackout prevention). Delivers cost savings and grid stability with zero historical training — perfect for off-grid or low-income homes.

3. Assistive Robotics & Prosthetics Control
Real-time joint/torque resolution for prosthetic limbs, exoskeletons, and mobility aids. Adapts instantly to user weight, terrain, or fatigue without retraining — emphasizing safety and smooth motion.

4. Companion Robots & Emotional Support
Governs context-aware, affectionate behavior (touch timing, tone, gaze) in humanoid robots for elderly care and loneliness reduction. Enforces strict consent, safety, and consistency constraints — reliable and explainable.

5. Personalized Education & AI Literacy Tools
Privacy-preserving adaptive curricula that sequence lessons from known prerequisites and attention limits — no data collection. Ideal for homeschooling, teaching real AI decision skills to kids in underserved communities.

6. Hospital & Public Health Resource Allocation
Optimizes beds, staffing, triage, and drug distribution under ethical, capacity, and urgency constraints. Provides auditable, real-time decisions for overwhelmed facilities or public health crises.
7. Environmental Conservation & Wildlife Protection
Plans optimal drone patrol routes and resource deployment for anti-poaching and ecosystem monitoring using known animal behavior and terrain constraints.

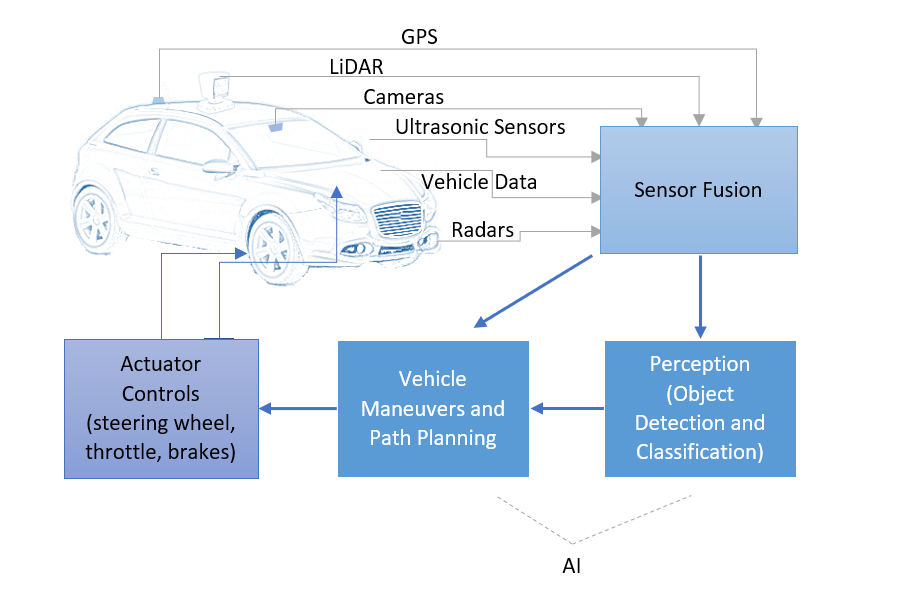
8. Autonomous Vehicle Governance & Safety Layers
Serves as the deterministic "brakes and steering" overlay — enforcing safety, policy, and comfort constraints on top of perception models in real time.
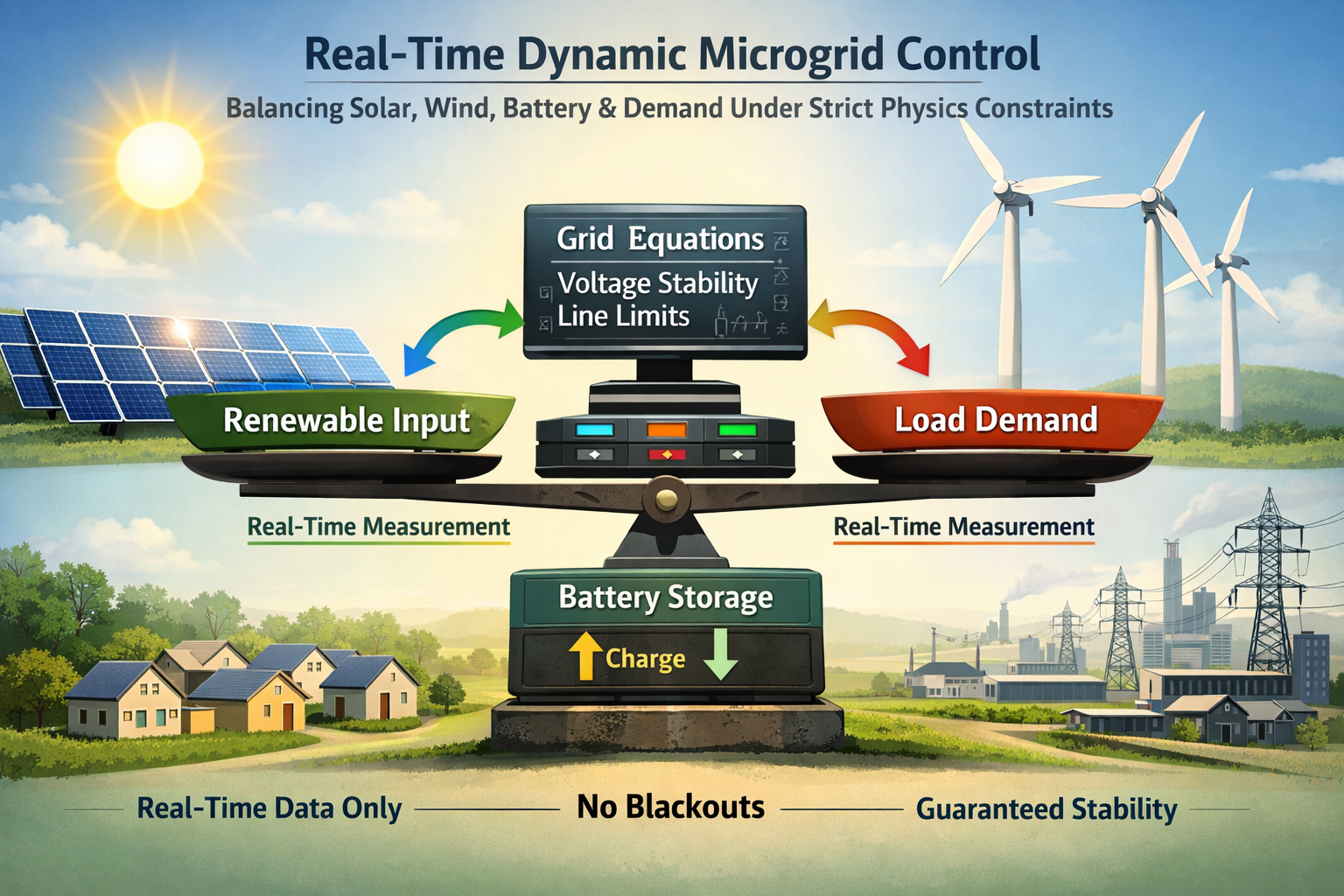
9. Smart Grid & Renewable Energy Balancing (GridZero)
Dynamically balances solar/wind input, battery charge/discharge, and demand under strict physics constraints (voltage stability, line limits, no blackouts) using only real-time measurements and known grid equations — no historical load profiles or learned forecasting models required. Ideal for microgrids, off-grid communities, and utility-scale renewable integration where explainability and guaranteed stability matter most.
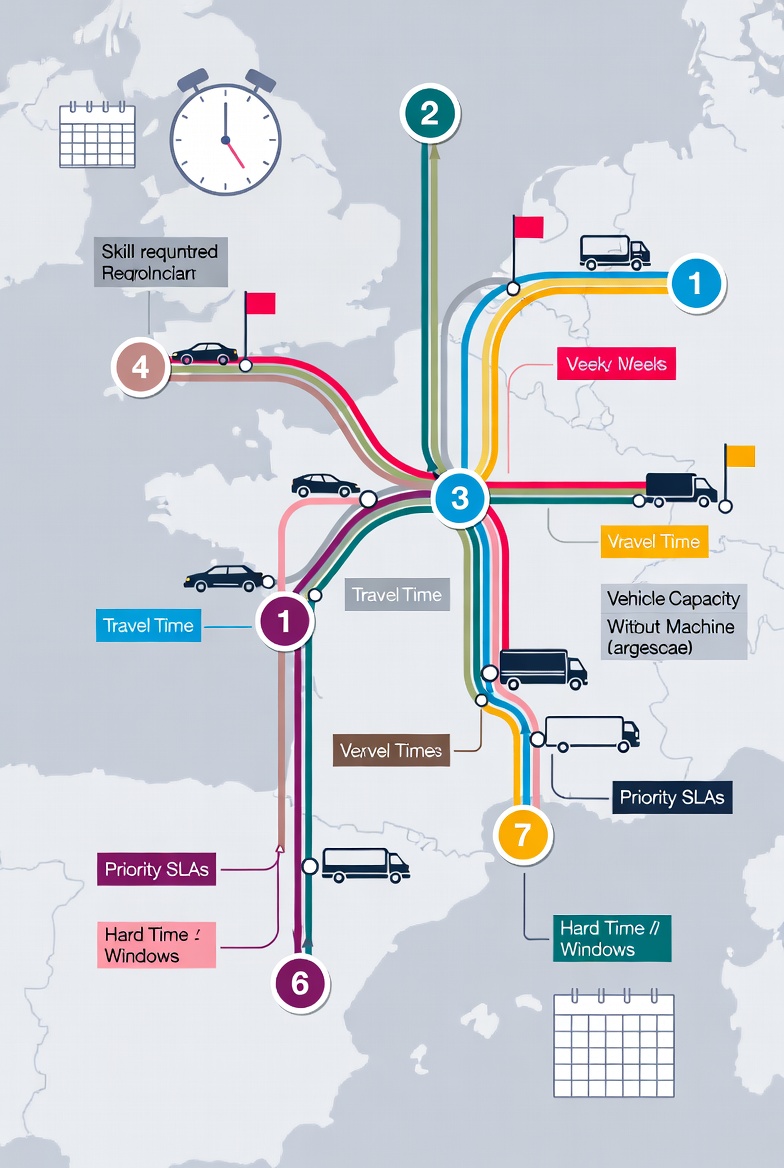
10. Large-Scale Field Service & Preventive Maintenance Routing
Schedules and routes hundreds of technicians across cities/regions over weeks/months while respecting technician skills, travel time, vehicle capacity, priority SLAs, and hard time windows — all deterministically resolved from current constraints without training on past tickets. Used by utilities, telecoms, and facility management firms to minimize downtime and travel costs at massive scale.
11. Critical Infrastructure Safety Governor (FailSafe Layer)
Acts as a deterministic overlay on any autonomous or semi-autonomous system (drones, vehicles, industrial robots, power plants) — instantly enforces hard safety invariants, ethical boundaries, and regulatory constraints in real time even when perception/ML layers produce uncertain outputs. Guarantees "never violate X" properties mathematically.

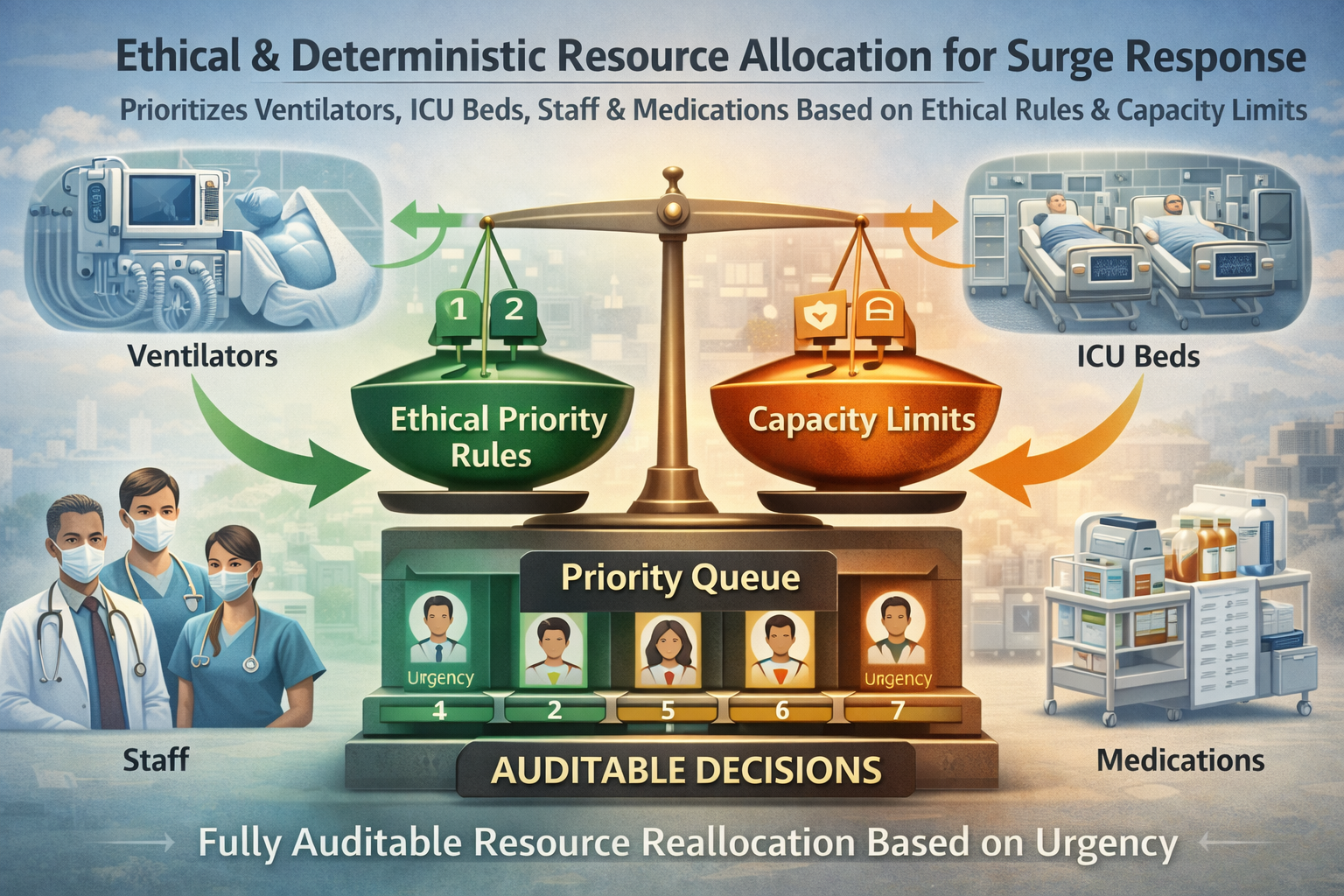
12. Crisis Hospital Resource & Triage Resolver
In mass-casualty or pandemic surge scenarios, instantly re-allocates ventilators, ICU beds, staff, and medications across patients/units under ethical priority rules, capacity hard-limits, and urgency scores — fully auditable and deterministic so decisions can be reviewed and trusted by medical boards.
These applications are not exhaustive — the framework is domain-agnostic and can be adapted rapidly to new problems where structure is known and determinism is essential. Ongoing development focuses on open-source expansion, more live demos, and community contributions.
Conclusion
Zero-Training AI™ proves that intelligence does not require massive datasets, retraining cycles, or opaque inference. When constraints and objectives are explicit, optimal decisions can be resolved mathematically — reliably, explainably, and in real time.
All code is open source under Apache license. The framework is free for anyone to use, extend, and apply — from nonprofits and educators to developers and researchers.
The future of this work is collaborative and open — let's build deterministic intelligence that benefits everyone.